

(no amplified dynamic microphone has a to low output voltage to work. Using an electred microphone is shown (in gray) in the diagram below. You can connect the circuit to the an electred microphone or amplified dynamic microphone. Thanks for reading and hope this helps you learn more about FM transmitters! Leave a comment below if you have any questions.In this project, you will make a simple 3-stage low-power broadcast-type circuit, using a crystal oscillator integrated circuit and an a collector modulated AM oscillator with amplifier. To get this inductance, we will need a wire coil about 12mm long with a diameter of about 9mm, and with five turns of magnet wire. So the inductance of L1 needs to be 0.127uH for its reactance to match the reactance of variable capacitor C5. Now we can calculate the inductance of L1 requred to get a reactance of 79.6Ω: We can rearrange this formula to solve for inductance: This formula relates reactance to inductance: Now that we know the reactance of the capacitor, we can calculate the inductance of L1 that will provide 79.6Ω of reactance.

With variable capacitor C5 adjusted to about 20pF and broadcasting at 100MHz, the reactance of capacitor C5 would be: To calculate the reactance of a capacitor, use this formula: First we need to design a wire coil for L1 that has the same reactance as the capacitor at this frequency. Capacitor C5 should be in the 10pF to 50pF range.įor example, let’s say we wanted to broadcast an FM radio signal at a frequency of 100MHz. The frequency can be adjusted by turning variable capacitor C5. The frequency that is transmitted is controlled by the resonance of the tuned circuit formed between L1 and C5. You could also use a dipole antenna, or two wires stretched out in opposite directions, each side being λ/4. To find the length of a quarter wavelength: So for a 100MHz output frequency, the wavelength is: How long is a quarter of a wavelength (λ)? But to be academically perfect, this would entail a sheet of conducting material at least a quarter of a wavelength in radius about the vertical.
C200i transistor fm how to#
How to Build the AntennaĪ simple vertical antenna working against a ground plane will suffice.
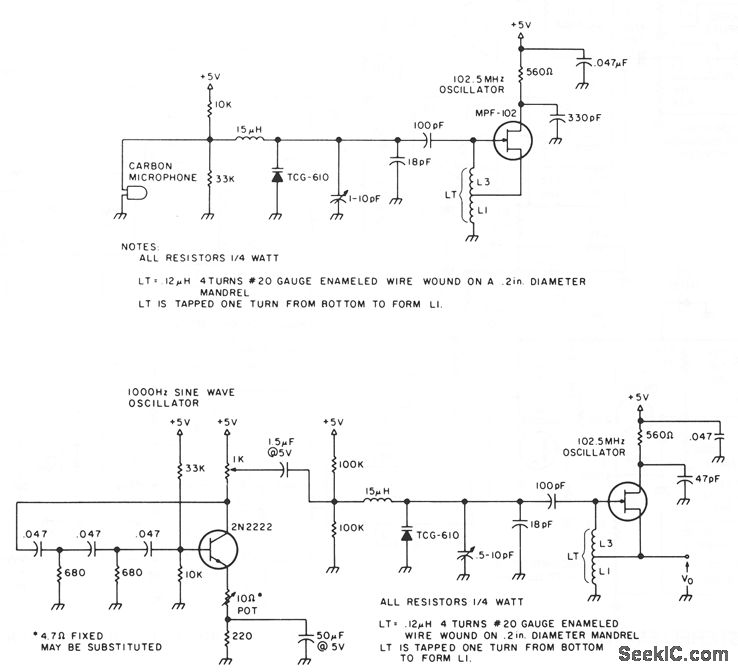
Transistor Q2 also acts as a power amplifier and feeds the frequency modulated audio signal to the antenna through capacitor C7. The LC circuit created by L1 and C5 determines the frequency of oscillation on the collector of Q2, which can be tuned to a frequency in the FM broadcast band by adjusting variable capacitor C5. Since there is no phase shift between the emitter and collector in a common base circuit, C6 provides feedback and causes the circuit to oscillate. For example Q1 could be a BC239C bipolar NPN transistor, and Q2 could be a 2N5179 VHF transistor.Ġ.01uF capacitor C4 grounds the base of transistor Q2, making this a common base circuit. Use transistors with an fT of at least 200MHz. This is a very high frequency (VHF) circuit, so you will want to use transistors with a high maximum operating frequency (fT). The output of Q1 is fed into the frequency modulating circuit created by transistor Q2, inductor L1, and variable capacitor C5. Transistor Q1 is a high gain audio amplifier that amplifies the sound detected by the electret microphone. The circuit is powered by a 9V power supply. Here is the schematic for the FM transmitter we are going to build: However, the range is highly dependent on the efficiency of the antenna. In my testing, it has a range of about 50 meters. The FM transmitter we are going to build works quite well.

Take a look at our article on How to Build an AM Radio Transmitter if you’re interested in building an AM transmitter. AM radio signals are broadcast between a range of about 550kHz to 1720kHz, while FM signals are broadcast at a range between about 88MHz to 108MHz. In an FM transmitter, the amplitude is constant, but the frequency is modulated (frequency modulation).Īnother difference between AM transmitters and FM transmitters is the frequency at which they broadcast radio signals. In an AM transmitter, the radio signal is modulated up and down in amplitude while the frequency remains constant (amplitude modulation). One difference between AM and FM transmitters is how modulation is superimposed on the radio signal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
